Inspecting an AST
Inspecting an AST
Two of the more common questions on JavaParser are:
- If I have this piece of code, how do I access that part of it?
- If I want this piece of code, how do I create the AST for it?
and both can be answered the same way: by looking at the AST that is generated when you parse the code you have or want. We offer several ways to do this.
First: parse the code
This is something like:
package com.github.javaparser;
import com.github.javaparser.ast.CompilationUnit;
public class Inspect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Parse the code you want to inspect:
CompilationUnit cu = StaticJavaParser.parse("class X { int x; }");
// Now comes the inspection code:
System.out.println(cu);
}
}
Option 1: your IDE’s debugger
You’ll need to figure out how your IDE works to get this to work. Put a breakpoint on System.out.println(cu); and run the program in debug mode. When it stops at the breakpoint, you should be able to see the known variables. Look for cu and you can click it open, and now you can inspect the whole generated AST.
Option 2: use one the structure printers
Thanks to Ryan Beckett there are a few printers that will output the structure of the AST with only one purpose: for you to look at. My favourite one outputs Yaml:
// Now comes the inspection code:
YamlPrinter printer = new YamlPrinter(true);
System.out.println(printer.output(cu));
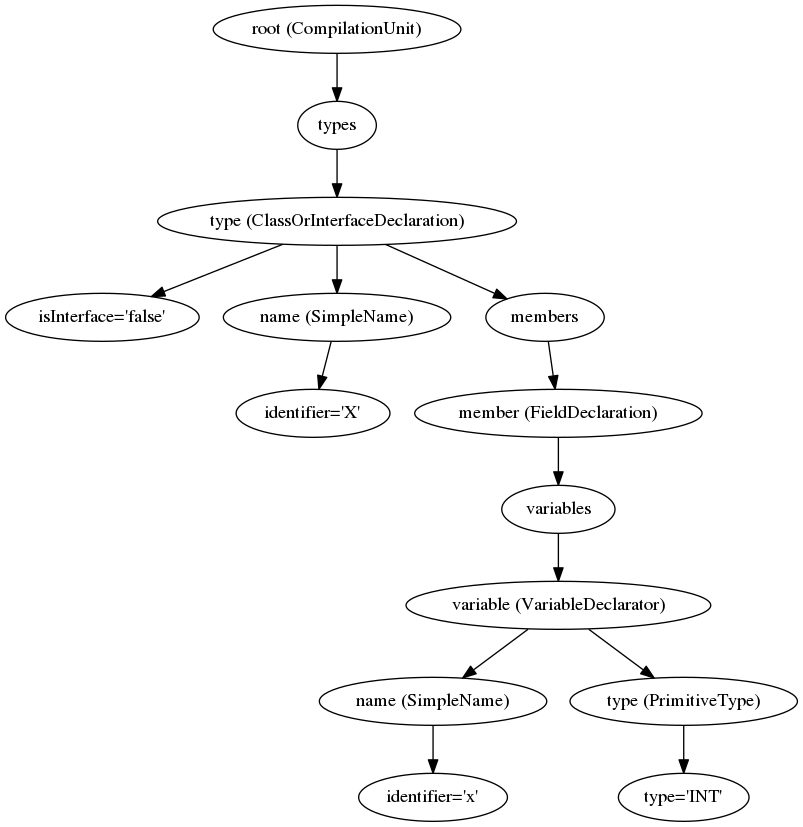
Here’s the output. You can see property names (isInterface, identifier, …) node types (Type=CompilationUnit) and values ("false", "x"). You can see how a type has members, how int x; is one of those members, that it has type FieldDeclaration and can contain multiple variables, but there is only one now: "x".
root(Type=CompilationUnit):
types:
- type(Type=ClassOrInterfaceDeclaration):
isInterface: "false"
name(Type=SimpleName):
identifier: "X"
members:
- member(Type=FieldDeclaration):
variables:
- variable(Type=VariableDeclarator):
name(Type=SimpleName):
identifier: "x"
type(Type=PrimitiveType):
type: "INT"
If you like looking at XML, try:
// Now comes the inspection code:
XmlPrinter printer = new XmlPrinter(true);
System.out.println(printer.output(cu));
You will need to load this into an editor that can format XML. Finally an extra cool one - it outputs the AST as a dot file which can be visualized as a graph with Graphviz!
// Now comes the inspection code:
DotPrinter printer = new DotPrinter(true);
try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("ast.dot");
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(fileWriter)) {
printWriter.print(printer.output(cu));
}
I’ve sent the output to Graphiz this way:
dot -Tpng ast.dot > ast.png